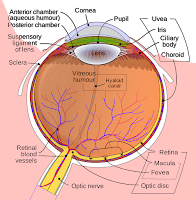
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada
(VKH) syndrome is a bilateral granulomatous uveitis that typically presents
with distinct clinical features based on the duration and stage of the disease.
The acute stage of VKH is characterized by diffuse choroiditis, multifocal
areas of subretinal fluid and/or bullous serous retinal detachments, with or
without neurologic (headaches, meningismus) or auditory (tinnitus, hypoacusia)
symptoms.
The convalescent stage of the disease develops 12 weeks after onset
and is characterized by resolution of retinal detachments with disappearance of
cells from the anterior chamber and the vitreous, with characteristic
pigmentary changes in the macula and sunset glow fundus. The chronic/recurrent
phase is characterized by clinical signs of disease activity in the anterior
segment of the eye with anterior granulomatous uveitis and dermatologic signs
(vitiligo, alopecia, poliosis).
First
described by Robertson in 1973. RAMs are acquired, localised dilatations of an
arteriole within the radius of the 3rd branch of the retinal arterial tree.
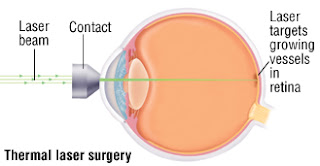
Current treatment options are controversial and of unproven benefit. We present
the case of a 76-year old gentleman with progressive vision loss from a
unilateral RAM who responded favourably to treatment with PDT using Verteporfin.
To the best of our knowledge, there are no previously published reports on the
use of PDT in treating RAM.
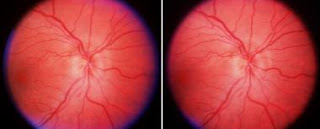
Ischaemic
optic neuropathy (ION) is the commonest adult optic nerve disorder encountered
worldwide and can be expected to increase in incidence in our ageing
population. The condition has been classified as a) anterior (AION) affecting the optic nerve head and b) posterior (PION) involving that portion of the
optic nerve behind its immediate retrolaminar portion. Furthermore there are
two pathological varieties of the disease c) Arteritic (AAION) almost
exclusively associated with Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) and d) Non arteritic
(NA-AION or less correctly NAION) usually associated with diabetes,
hypertension and hyper cholesterol laemia. A recent treatise on the subject
runs to more than 600 pages.
Hunter syndrome or
mucopolysaccharidosis type II is a rare progressive multi-systemic disorder,
caused by an abnormal storage of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in almost every cell
type, including most ocular tissues. Patients have a short life expectancy and
ocular manifestations can be present early in the course of disease. To report the fund us auto fluorescence and tomographic ocular findings in Hunter syndrome. A 18-year-old male patient with Hunter syndrome with progressive
nyctalopia was submitted to color fundus photography, blue fundus auto fluorescence
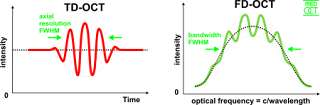
(FAF), fluorescein angiography (FA) and spectral domain optical coherence
tomography with enhanced-depth imaging (EDI-SD OCT).
Age-related macular degeneration
(AMD) is a leading cause of irreversible vision loss among people age 50 and
older. Based on the presence or absence of blood vessels, it is classified intotwo types, wet and dry. In the past decades, significant progress has been made
in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying wet AMD, and several
robust therapeutic drugs were developed to block the development of new blood
vessels and leakage from the abnormal vessels with favorable clinical effect.

In
contrast, there are no approved treatments for dry AMD and the mechanisms are
not completely known. However, it has been approved that genetics, complement
dysregulation, oxidative stress, mitochondria DNA damage were involved in the mechanisms. Variety of scientific studies, including gene replacement therapy,
retinal cell transplantation, pharmaceutical intervention and vitamin dietary
supplementation, hold promise in developing treatment to prevent or slow the
progression of the disease. In the clinical aspect, multiple clinical studies
and trials have been done to further our knowledge of AMD, and on-going studies
are raising hopes for improved treatments.
Purpose: We reported a rare case of
bilateral chronic central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR) induced by longterm
exogenous testosterone treatment. Method: A case report. Result: A 52-year-oldman with medical history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, diabetes insipidus
and hypogonadism presented to our ophthalmologic clinic with unstable blurred
vision of right eye for more than 5 years and vision loss of left eye since
childhood injury. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed subfoveal fluid in
both of his eyes.